Tree-planting reduces sandstorms in Kashgar
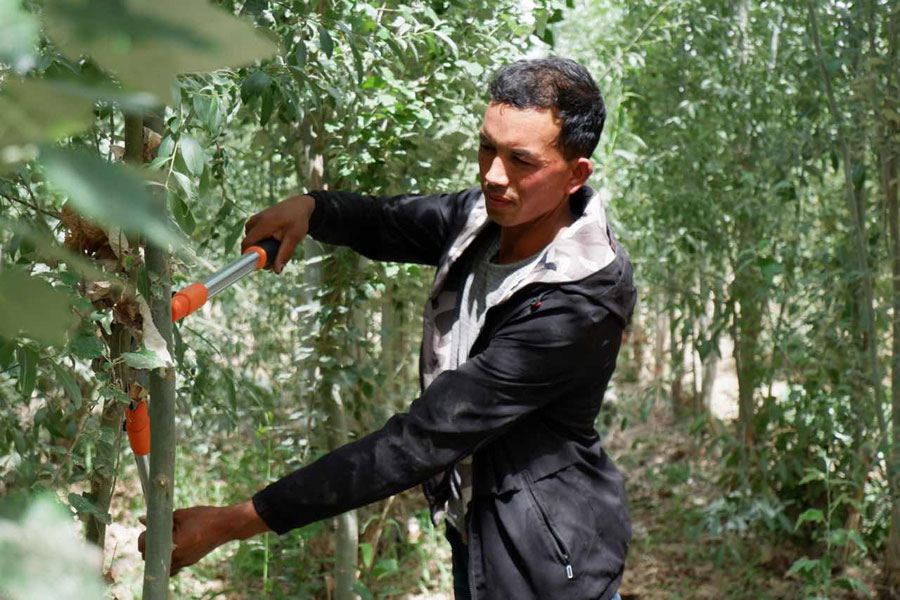


Desert conversion projects in southern Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region have worked to contain sandstorms on the outskirts of the Taklamakan Desert over the past few years.
The projects also bolster cash crop farming by offering much-needed farmlands, injecting momentum into sweeping poverty relief efforts in one of China's least developed regions.
The local government of Makit county in Kashgar is charging ahead with a project that aimed at converting about 66,000 hectares of dunes into arable lands by planting drought-resistant plants like saxaul and poplar.
To that end, 50-meter-wide belts of poplar were planted in a bid to reduce wind erosion in the Uyghur-dominated region according to Wang Yufeng, the director of the county's natural resources bureau who oversaw the project over the last seven years.
Meanwhile, many saxaul trees were also planted between the poplar belts to improve the land condition, he said.
"So far we have completed about 22,000 hectares, with more than 190 million trees planted," he said, adding this has already begun to reap ecological benefits.
- World Television Day celebrated with conference in Shanxi
- University launches new AI department to align with national priorities
- Jilin kicks off 2025-26 snow season with grand opening event
- China hails 'hard-won' COP30 Global Mutirao decision
- China-SA science exhibition showcases innovation, cultural exchange
- China opens draft regulations on data protection to public consultation